Apple has published a new clinical validation summary document that explains how its new sleep apnea detection feature works on Apple Watch. Sleep apnea monitoring is part of Apple Watch Series 10 and comes to Apple Watch Ultra 2 and Apple Watch Series 9 with watchOS 11. The new watch hardware launches on Friday, and watchOS 11 is available now.
A common point of interest is what sensor Apple Watch uses for detecting signs of sleep apnea. Apple Watch users the 3-axis gyroscope to detect disturbances in breathing while sleep tracking. The blood oxygen sensor, which is disabled on newer watches in the US but otherwise available worldwide, is not used.
Support for monitoring and providing alerts when signs of sleep apnea are detected is a feature that requires regulatory approval in regions where offered. As promised, Apple received the necessary approval for its accelerometer-based breathing disturbance monitoring in the US. In other words, you don’t just have to take Apple’s word for it that this method works.
The newly published documentation goes into more detail about how Apple’s approved sleep apnea detection feature works:
Apple Watch tracks movement with triaxial accelerometer signals, which capture coarse motion of the body as well as fine movements including motion associated with breathing. Apple developed an algorithm that uses the accelerometer time series data to classify Breathing Disturbances that occur during sleep tracking, which are temporary interruptions in the breathing pattern. Figure 1 demonstrates the relationship of the Apple Watch accelerometer data (X, Y, and Z) alongside more traditional methods of identifying disruptions to breathing, including abdomen belts and airflow meters.
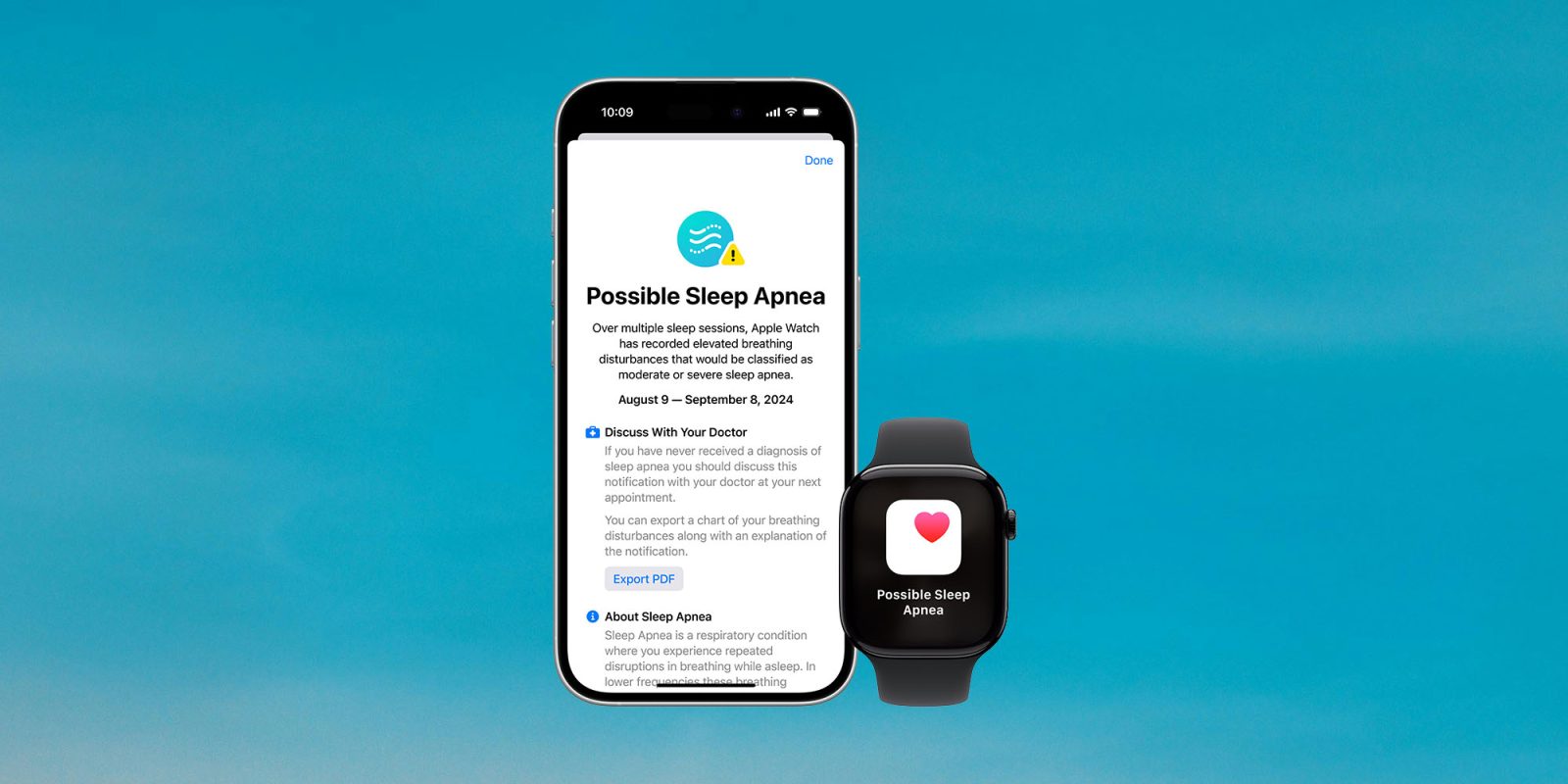
The Sleep Apnea Notification Feature contains two components: a nightly Breathing Disturbances measurement and a notification sent to the user if the Breathing Disturbances values are elevated over a 30-day period, indicating signs of potential moderate to severe sleep apnea. Note that neither component is intended or cleared for use by people who are already diagnosed with sleep apnea. Breathing Disturbances aren’t equivalent to the AHI.
Initial use of this feature requires a short onboarding process and sleep tracking to be enabled on Apple Watch. Once active, Breathing Disturbances values can be viewed in the Health app. Tracking Breathing Disturbances helps users understand their sleep and the behaviors or lifestyle factors that may affect their Breathing Disturbances levels. The notification feature alerts users who may be at risk of moderate to severe sleep apnea. An example of Breathing Disturbance data viewed in the iPhone Health app is shown in Figure 2. In this example, the majority of nights were classified as not elevated, so the displayed period is summarized as Not Elevated.
The full document contains more information about how sleep data was collected, the feature’s clinical validation, relevant references, and more. Check it out here.
Follow Zac: X, Threads, InstagramFTC: We use income earning auto affiliate links. More.

 3 months ago
45
3 months ago
45


![Ottocast elevates the connected car experience with wireless CarPlay AI Box, CloudSIM, Car TV Mate Pro, more [20% off]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2024/12/ottocast2.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)





 English (US) ·
English (US) ·